Stainless steel bearings
Cedinox
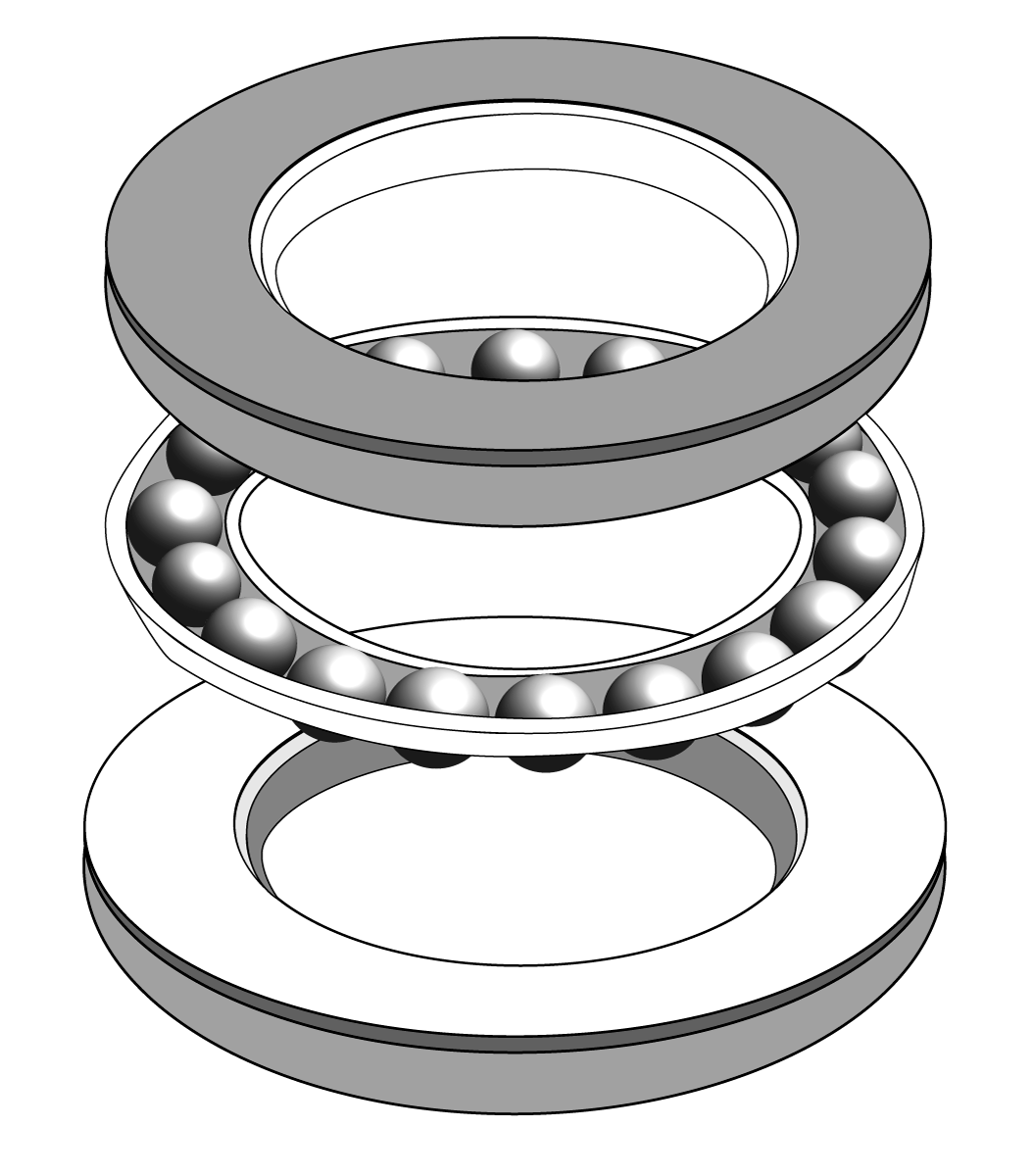
The bearing is the element that minimizes the friction that occurs between the shaft and the parts that are connected to it. This piece is formed by a pair of concentric cylinders separated by a crown of rollers or balls that rotate freely.
The balls are a vital element of the bearing, and their manufacture in stainless steel ensures a promising solution obtaining excellent results. Stainless steel balls are resistant to corrosion when exposed to moisture and other diverse environments.
Manufacturing process of the balls for bearings.
- The balls are produced from thick stainless steel wire.
- This wire is cut into pieces.
- A mould makes them rougher balls.
- They are processed through a grinder that eliminates irregularities.
- They are given a rounded shape and polished to a mirror finish.
- They pass through a furnace where the balls harden.
- The production process of balls ends with a cleaning solvent bath.
After the necessary quality controls, the balls are ready to pass to the machine of automatic assembly of the bearings.
Types of ball bearings:
- Deep groove ball bearings: they have a wide field of application. Their designs are simple and with no detachable parts, suitable for high speeds of operation, and they also require little maintenance.
- Self-aligning ball bearing: they have two rows of balls with a common spherical raceway in the outer ring of the bearing. This last feature makes the bearing self-aligning, allowing angular deviations of the shaft from the support. Suitable for applications where shaft misalignment or deformation may occur.
- Angular contact ball bearings: they have the rolling paths of their inner and outer rings offset from each other with respect to the axis of the bearing. They are particularly useful for supporting combined loads.
- Axial deep groove ball bearings: they can be single acting or double acting. The single-acting ones are suitable for absorbing axial loads and fixing the shaft in one direction, and can withstand small radial loads. The double-acting models are suitable for absorbing axial loads and fixing the shaft in both directions. However they do not support radial loads.